LeetCode Exercise

This is my LeetCode exercise.
You can see all question I did here.
tags: leetcode hard Dynamic Programming Tree Depth-First Search Binary Tree
124. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
Description
A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Examples
Example 1:
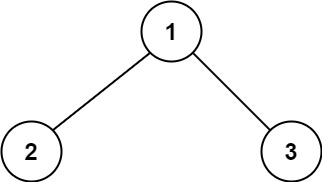 Input: root = [1,2,3]
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
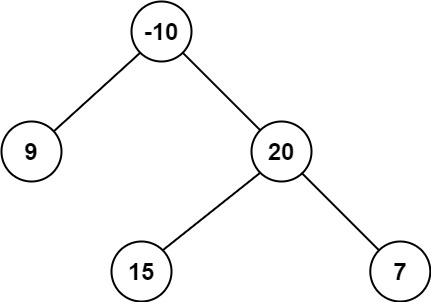 Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range $[1, 3 * 10^4]$.
- $-1000 \leq Node.val \leq 1000$
Code
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
typedef struct TreeNode TNODE;
#define CASE_MIN -1001
#define MAX(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
// Find the depth from root to leaf
int DEPTH_MAX_SEARCH(TNODE* root, int* crossMax) {
// If node is null, return CASE_MIN
if (!root)
return CASE_MIN;
int left = DEPTH_MAX_SEARCH(root->left, crossMax);
int right = DEPTH_MAX_SEARCH(root->right, crossMax);
// No-child leaf return its value
if (left == CASE_MIN && right == CASE_MIN)
return root->val;
int maxChild = MAX(left, right);
// Avoid child having CASE_MIN, using maxChild as filter
*crossMax = MAX(*crossMax, maxChild);
*crossMax = MAX(*crossMax, root->val);
*crossMax = MAX(*crossMax, (left + right + root->val));
return MAX((maxChild + root->val), root->val);
}
int maxPathSum(struct TreeNode* root) {
int crossMax = CASE_MIN;
int depthMax = DEPTH_MAX_SEARCH(root, &crossMax);
return MAX(crossMax, depthMax);
}
Complexity
| Space | Time |
|---|---|
| $O(1)$ | $O(N)$ |
Result
- Runtime : 18 ms, 95.54%
- Memory : 13.6 MB, 50.89%